Unlocking the Earth's Secrets: Understanding Geological Maps with ArcGIS StoryMaps
Table of Contents
- Geographical position of investigated area and generalised geologic map ...
- (a) Schematic geological map (modified and readapted after ...
- PPT - Geological Mapping techniques to enhance mineral exploration ...
- St Johns Campus Map - Korry Mildrid
- Geological Map, Section 4-1
- Geological Map of the studied area and near surrounding (Modified from ...
- A Natural History of Paddock Wood in 2016: Geology & Hydrology
- Simplified geological map of the study area shows four... | Download ...
- Mapping Earth's History with an Eye on the Future - The Bridge ...
- Geology map of the study area (Modified from Minerals and Geoscience ...
Geological maps are a crucial tool for understanding the Earth's composition, structure, and history. These maps provide a visual representation of the geological features of an area, including the distribution of different rock types, faults, folds, and other geological phenomena. In this article, we will explore what a geological map is, its importance, and how ArcGIS StoryMaps can be used to create and share interactive geological maps.


What is a Geological Map?

A geological map is a type of map that shows the geological features of an area, including the types of rocks, minerals, and landforms present. Geological maps are created by geologists who collect data through field observations, laboratory analysis, and remote sensing techniques. The data is then used to create a map that shows the distribution of different geological features, such as rock units, faults, and folds.


Key Components of a Geological Map

A geological map typically includes several key components, including:

- Rock units: These are areas of the map that are colored or patterned to represent different types of rocks, such as sedimentary, igneous, or metamorphic rocks.
- Faults: These are lines on the map that indicate the location of faults, which are fractures in the Earth's crust where rocks on either side have moved past each other.
- Folds: These are areas of the map that show the location of folds, which are bends in the Earth's crust that can indicate the presence of tectonic activity.
- Geological symbols: These are symbols used to represent different geological features, such as strike and dip symbols, which indicate the orientation of rocks.
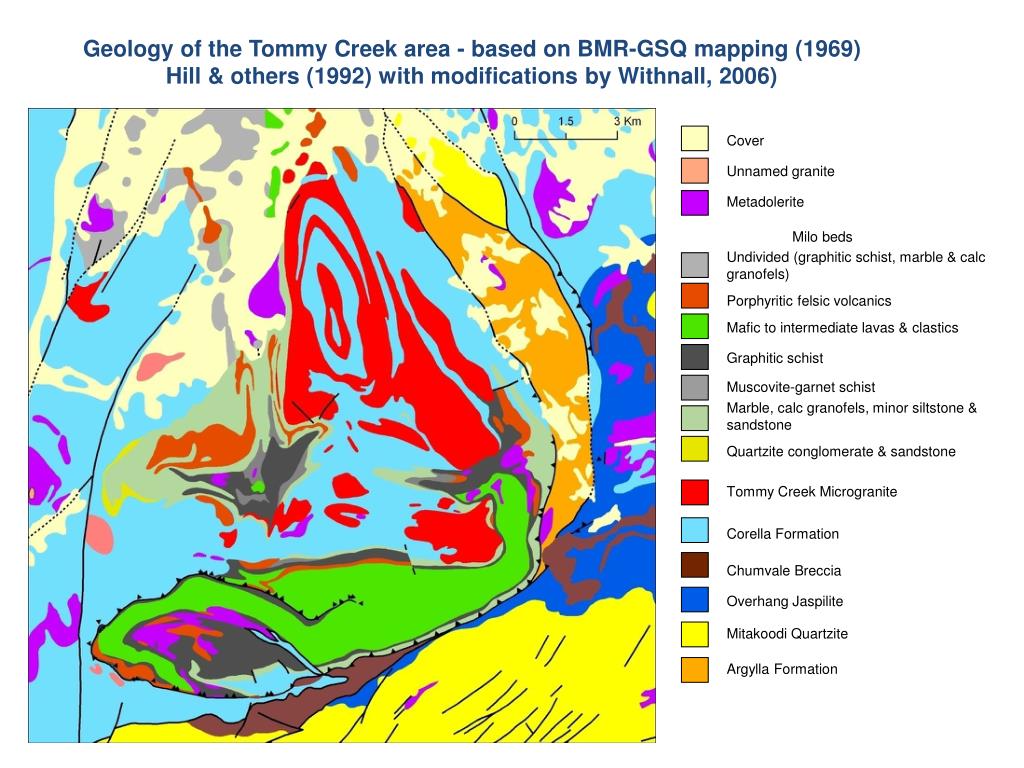
The Importance of Geological Maps
Geological maps are essential for a wide range of applications, including:
- Natural resource management: Geological maps can help identify areas with potential for mineral or energy resources.
- Environmental monitoring: Geological maps can help track changes in the environment, such as the movement of groundwater or the spread of pollution.
- Infrastructure planning: Geological maps can help identify areas that are prone to geological hazards, such as landslides or earthquakes.

Creating Interactive Geological Maps with ArcGIS StoryMaps
ArcGIS StoryMaps is a powerful tool for creating and sharing interactive geological maps. With ArcGIS StoryMaps, users can combine maps, text, images, and other media to create engaging and informative stories about the Earth's geology. Interactive geological maps can be used to:
- Visualize complex geological data: Interactive maps can help users understand complex geological concepts, such as the movement of tectonic plates or the formation of mountain ranges.
- Share knowledge and collaborate: Interactive maps can be shared with others, facilitating collaboration and knowledge-sharing among geologists, researchers, and stakeholders.
- Communicate geological information to the public: Interactive maps can be used to communicate geological information to the public, helping to raise awareness about geological hazards and the importance of geological conservation.
In conclusion, geological maps are a vital tool for understanding the Earth's composition, structure, and history. With the help of ArcGIS StoryMaps, users can create and share interactive geological maps that visualize complex geological data, facilitate collaboration and knowledge-sharing, and communicate geological information to the public.
By leveraging the power of ArcGIS StoryMaps, geologists, researchers, and stakeholders can work together to unlock the Earth's secrets and better understand the complex geological processes that shape our planet.